Most of the time, we do not bother to learn about the minute details of an electrical circuit and tend to call for professional help when something goes wrong. However, it is necessary for organizations having a separate team for electrical system management to know these details so that they can handle the situation in times of emergency.
This article will provide in-depth information about capacitors, their functions, and uses in an electrical circuit.
What is a Capacitor?

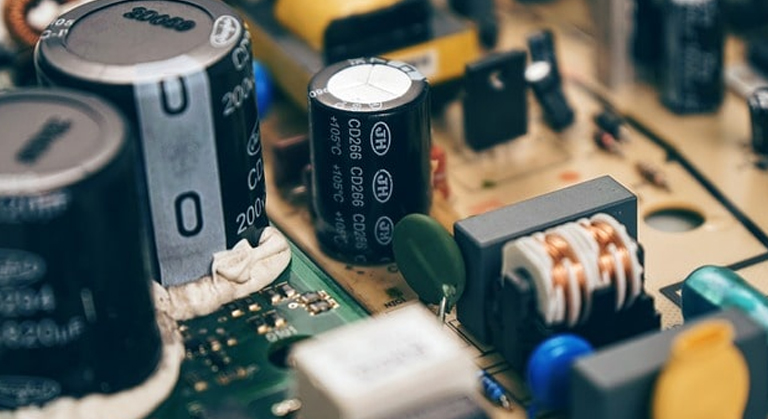
In layman’s terms, a capacitor is an electrical device that is fitted in electrical circuits to effectively store energy. There are two types of capacitors available in the market – non-polarized capacitor and polarized capacitor. There are various ways of connecting a capacitor and the electrical device can carry different numbers in a specific electrical circuit.
Capacitors connected in a series will attain the highest value. However, when connected in a parallel manner, their output will be the same. Capacitors are used in combination with other electrical devices like inductors and resistors and are also used to time various other electrical gadgets like motors, televisions, and fans.
Types of Capacitors
There are two broad categories of capacitors as mentioned before – polarized capacitors and non-polarized capacitors.
Polarized Capacitor:
Capacitors with distinctive negative and positive poles are called polarized capacitors. A capacitor unit is calculated in terms of capacitance, which in turn is quantified in terms of Farad. Generally, most of the capacitors come with minuscule values of Farad called pico-Farad and micro-Farad (uF). A capacitor can be designed in one of the two ways – axial or radial. While both the leads of a capacitor are on the same end in the radial design, in the axial design the leads are on the opposite ends of the capacitor. Polarized capacitors are bigger in size and are electrolytic in nature. They are mostly used for direct current circuits and come with a high capacitance.
Non-Polarized Capacitor:
As implied by the name, the majority of non-polarized capacitors do not come with a distinctly positive or negative pole, which is why they are also known as bipolar capacitors. Unlike the polarized capacitors, the non-polarized versions of the same are not electrolytic in nature and come with relatively small capacitance, measured in micro-Farads. Non-polarized capacitors are used for alternating current (AC) circuits and are generally made of either ceramic or mica. These bipolar capacitors are mostly used in motherboards, circuit boards, computers, and simple circuits. In terms of cost, the non-polarized capacitors are quite cheap compared to their polarized counterparts.
Factors to Consider While Choosing a Capacitor
There are several factors that determine the quality of a capacitor and you need to consider them all to get the best deal. Here are some of the major parameters based on which you can choose a capacitor:
Operating Voltage: Not all capacitors available in the market work on the same voltage. While the tantalum capacitors operate at lower voltages, other capacitors like the ceramic counterparts have a wide range of working voltage. Therefore, if you require a capacitor with high voltage, make sure you make the correct choice.
Value Range: The value range of a capacitor is a major determinant when it comes to deciding on the type of capacitor required for a specific function. Different capacitors have different value ranges. So ensure that you buy a capacitor that functions in a value range that can work for you and your organization.
Polarization: As stated above, there are two types of capacitors – polarized and non-polarized. This is a major factor associated with capacitor choice, and you should consider carefully which of the two types you require.
Temperature: While some capacitors are affected by temperature, there are others like the silver mica capacitors that are not affected by temperature. So, if you are looking to install capacitors for electrical gadgets like filters and oscillators, choose wisely.
Leakage Current: The level of insulation required differs according to the type of capacitor chosen. While some may need a high level of insulation, for others it may not be so essential. So choose a capacitor that has a leakage current matching your requirements.
Price: One of the four P’s of marketing, the price is a major determinant in all purchase decisions. So choose a capacitor that does not exceed your budget and is also not too low grade in terms of quality.
What Are Capacitors Used For?
There are different ways in which a capacitor can be used in electrical circuits:
Capacitors are capable of eliminating ripples. So, if a direct current line has spikes and ripples in it, one can use a big capacitor to even out the voltage levels by allowing the capacitor to absorb the spikes in the current line.
Many a time, capacitors are effectively used to store energy, which can then be used for enabling high speeds of electrical transmission. Big lasers often use such capacitors to emit instantaneous, bright flashes of light.
Capacitors are often used in electrical circuits as band fillers, low-pass as well as high-pass. As a band filler, the capacitor effectively enables the current and voltage to flow at a specific value, waveform, and frequency.
In Conclusion:
Capacitors are an essential part of any electrical circuit or gadget. Hopefully, the above-mentioned information will help you choose the right capacitor in accordance with your needs and requirements.